Accelerating fault detection with AI-on-the-edge

Predictive maintenance is becoming an important support technology for modern manufacturing. Compared to fixed preventive maintenance intervals, it helps reduce downtime, lower maintenance costs, and extend equipment lifetime. A key element in such strategies is condition monitoring: using sensors and data analysis to understand the health of machines in real time and detect issues before they escalate. In this blogpost we dive into acoustic monitoring and how, combined with AI-on-the-edge, it can be a cost-efficient step towards predictive maintenance.
Beyond vibration sensors: Acoustic monitoring as a non-invasive alternative
Vibration-based condition monitoring is widely used to assess rotating machinery such as gears and bearings. It relies on accelerometer-based sensors, which provide strong and reliable signals. However, these sensors can be expensive, invasive to install, and difficult to scale when multiple components must be monitored.
Acoustic condition monitoring has the potential to be a complementary and more cost-efficient option. Microphones allow companies to “listen” to machines without physical contact. They are easy to deploy and, in some cases, a single microphone can capture the behaviour of several components. This makes the approach attractive for complex machines with many moving parts.
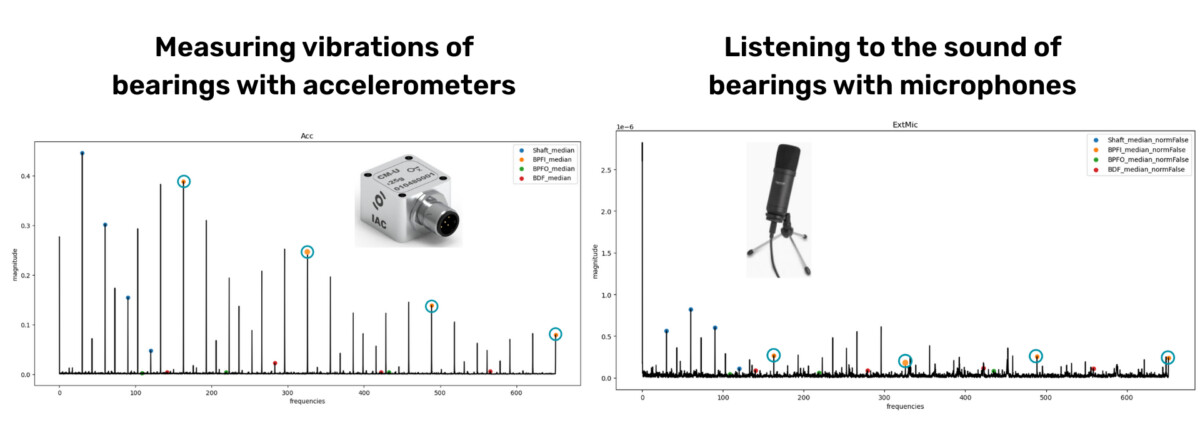
The challenge? Industrial environments are noisy. Microphone signals often suffer from a low signal-to-noise ratio because background disturbances easily mask the subtle acoustic signatures of bearings or gears. As a result, classical signal-processing methods can generate many false positives that suggest a fault even though the bearing is healthy. To extract useful information, we need support from Artificial Intelligence.
Reliable signals with AI-on-the-Edge
Using our Smart Maintenance test setup, we evaluated bearings and collected microphone data under controlled conditions. This allowed us to:
- assess the limitations of traditional signal processing in noisy environments
- train a deep neural network to distinguish between healthy and defective bearings
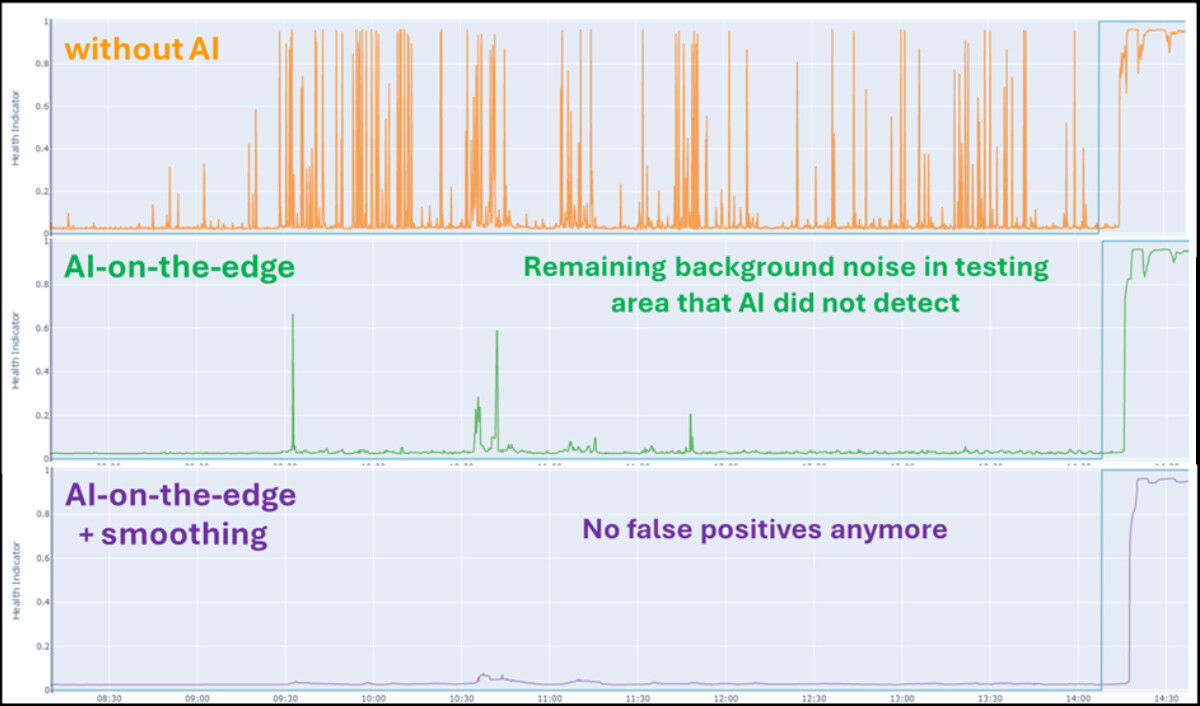
- add a noise-aware smoothing step to filter out false background signals
By training a neural network we were able to filter out most of the false positives. Remaining alerts typically stemmed from more complex background noise. With an additional noise-aware smoothing, we were able to remove those as well.
Improved maintenance decisions
Using microphones combined with a simple AI model, our tests show:
- almost 100% accuracy in detecting bearing faults
- a reduction by half in the average time needed to identify faults
Although acoustic monitoring is less familiar to many companies, it offers a practical extension to their predictive maintenance toolbox. It is cost-effective, non-invasive, easy to deploy, and suitable for a wide range of machines.
Sharing our findings with industry
Within the European-funded AI REDGIO 5.0 project, we demonstrated this approach to manufacturing companies. We moved AI-based data processing from the cloud to a stand-alone, portable measurement box. We showed how to run several AI models in parallel on-the-edge and how to train these models for early anomaly detection. This set-up enabled us to showcase both vibrational and acoustic condition monitoring in a realistic industrial context and to explore how AI-on-the-edge can support early anomaly detection.

Get in touch with our experts
Would you like to learn more about vibrational or acoustic condition monitoring, or about AI-on-the-edge data processing? Thinking about a feasibility study or assessing a business case?
Funded by


AI REDGIO 5.0 is an EU-funded project that supports the digital transformation of European manufacturing SMEs through AI-on-the-edge. Building on the Horizon 2020 I4MS and AI REGIO programmes, it connects 43 partners across 18 countries to help companies adopt practical, human-centric Industry 5.0 technologies. The goal: accelerating the uptake of AI and strengthens cross-regional collaboration — helping Europe move towards smarter, more sustainable and people-centred manufacturing.
At its core, the project focused on experimentation and collaboration. Three types of experiments were conducted. SME-driven experiments to demonstrate real-world AI applications improving productivity and agility in factories. Test-before-invest experiments, performed within Didactic Factories, Technology and Regulatory Sandboxes for AI (TERESAs), and Virtual Factories, refined AI tools and assess their ethical, regulatory, and human-centric dimensions.
Disclaimer: Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or European Health and Digital Executive Agency (HADEA). Neither the European Union nor HADEA can be held responsible for them.



